This post expands on my previous post Hierarchy Changes in ConfigMgr 2012 SP1 by adding R2-specific information. Note that the Active Directory schema extensions did not change from previous versions of ConfigMgr 2012 and ConfigMgr 2007. There's no need to extend the AD schema if it has already been extended for the mentioned previous versions.
Certificate Registration Point
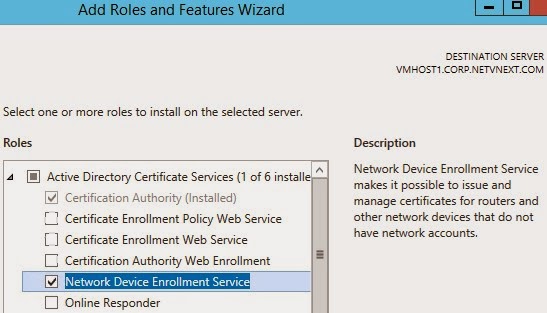
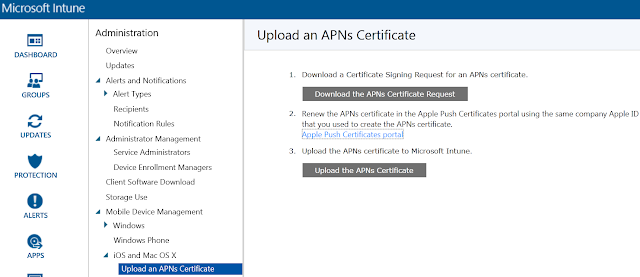
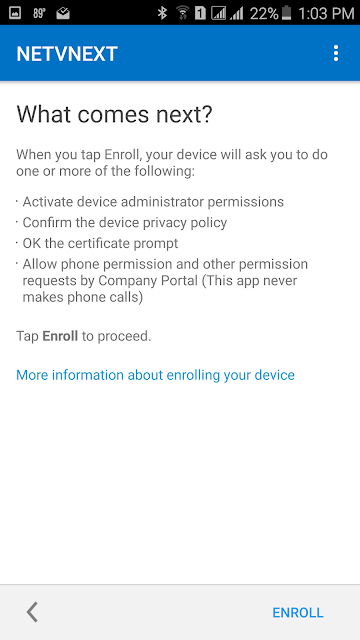
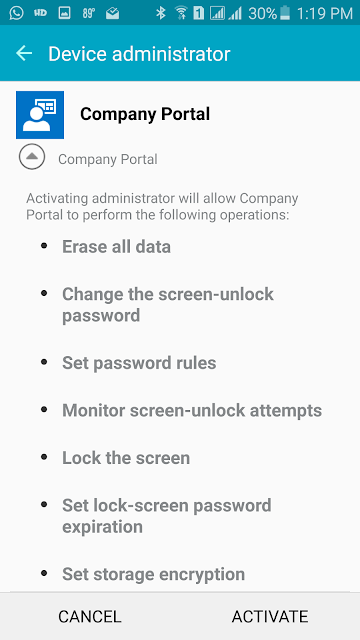
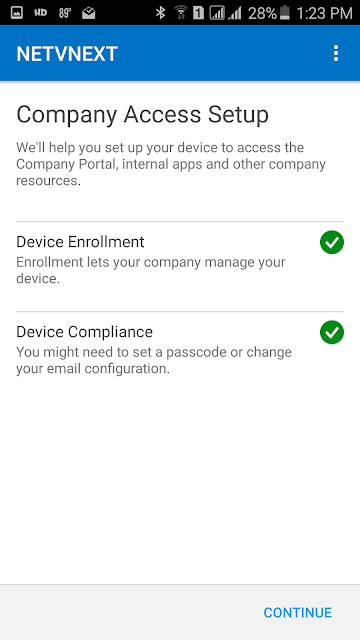
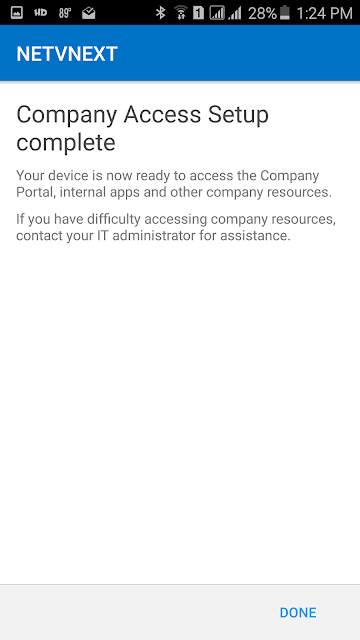
This is a new site system role that integrates with Active Directory (AD) certificate services and and the Network Device Enrollment Service role. The Network Device Enrollment Service role is part of the AD certificate services and must be installed and configured first. Note that the certificate services must be installed on Windows Server 2012 R2.
Next, the ConfigMgr Certificate Registration Point should be installed, which allows Configuration Manager the enrollment of authentication certificates to devices that it manages. This allows the ConfigMgr administrator to create and deploy certificate profiles necessary for users to initiate VPN and wireless connections on iOS, Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1 and Android devices.
After installing the Certificate Registration Point, the provided ConfigMgr Policy Module must be installed.You'll find the installation files in the following path of the ConfigMgr 2012 R2 installation media:
<ConfigMgrInstallationMedia>\SMSSETUP\POLICYMODULE\X64
The files are PolicyModule.msi and PolicyModuleSetup.exe.
Distribution Points on a Site
In SCCM 2012 RTM and SCCM 2012 SP1, each primary and secondary site supports up to 250 distribution points. In SCCM 2012 R2, each primary and secondary site supports up to 2000 additional distribution points configured as pull-distribution points. This means that the maximum number of supported distribution points on a site is 2250 with 2000 of those being pull-distribution points.
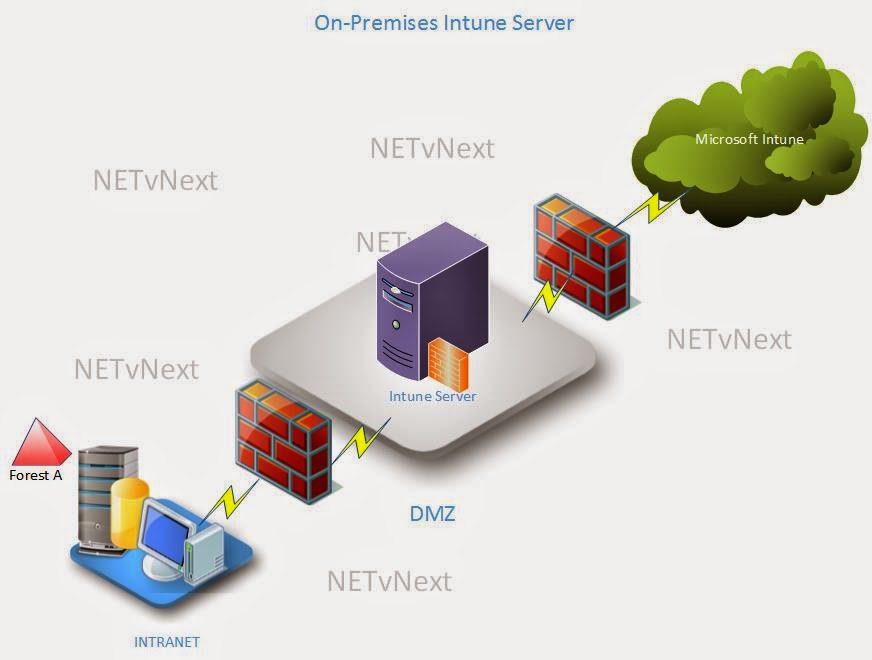
ConfigMgr and Windows Intune
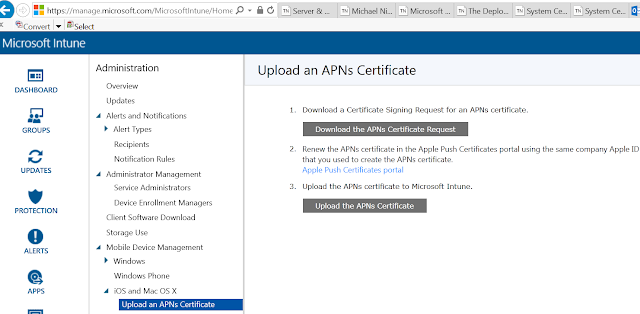
Although Windows Intune is not part of the ConfigMgr hierarchy, I'm adding this section because in my opinion anyone designing ConfigMgr hierarchies should be aware that integrating ConfigMgr 2012 R2 with the latest version of Windows Intune permits a deeper level of device management, such as granting the administrator more granular control. More details on this Microsoft blog post.
Certificate Registration Point
This is a new site system role that integrates with Active Directory (AD) certificate services and and the Network Device Enrollment Service role. The Network Device Enrollment Service role is part of the AD certificate services and must be installed and configured first. Note that the certificate services must be installed on Windows Server 2012 R2.
Next, the ConfigMgr Certificate Registration Point should be installed, which allows Configuration Manager the enrollment of authentication certificates to devices that it manages. This allows the ConfigMgr administrator to create and deploy certificate profiles necessary for users to initiate VPN and wireless connections on iOS, Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1 and Android devices.
After installing the Certificate Registration Point, the provided ConfigMgr Policy Module must be installed.You'll find the installation files in the following path of the ConfigMgr 2012 R2 installation media:
<ConfigMgrInstallationMedia>\SMSSETUP\POLICYMODULE\X64
The files are PolicyModule.msi and PolicyModuleSetup.exe.
Distribution Points on a Site
In SCCM 2012 RTM and SCCM 2012 SP1, each primary and secondary site supports up to 250 distribution points. In SCCM 2012 R2, each primary and secondary site supports up to 2000 additional distribution points configured as pull-distribution points. This means that the maximum number of supported distribution points on a site is 2250 with 2000 of those being pull-distribution points.
ConfigMgr and Windows Intune
Although Windows Intune is not part of the ConfigMgr hierarchy, I'm adding this section because in my opinion anyone designing ConfigMgr hierarchies should be aware that integrating ConfigMgr 2012 R2 with the latest version of Windows Intune permits a deeper level of device management, such as granting the administrator more granular control. More details on this Microsoft blog post.
SCCM